New scientific paper, the result of a collaboration between the Institute and the Faculty of Medicine
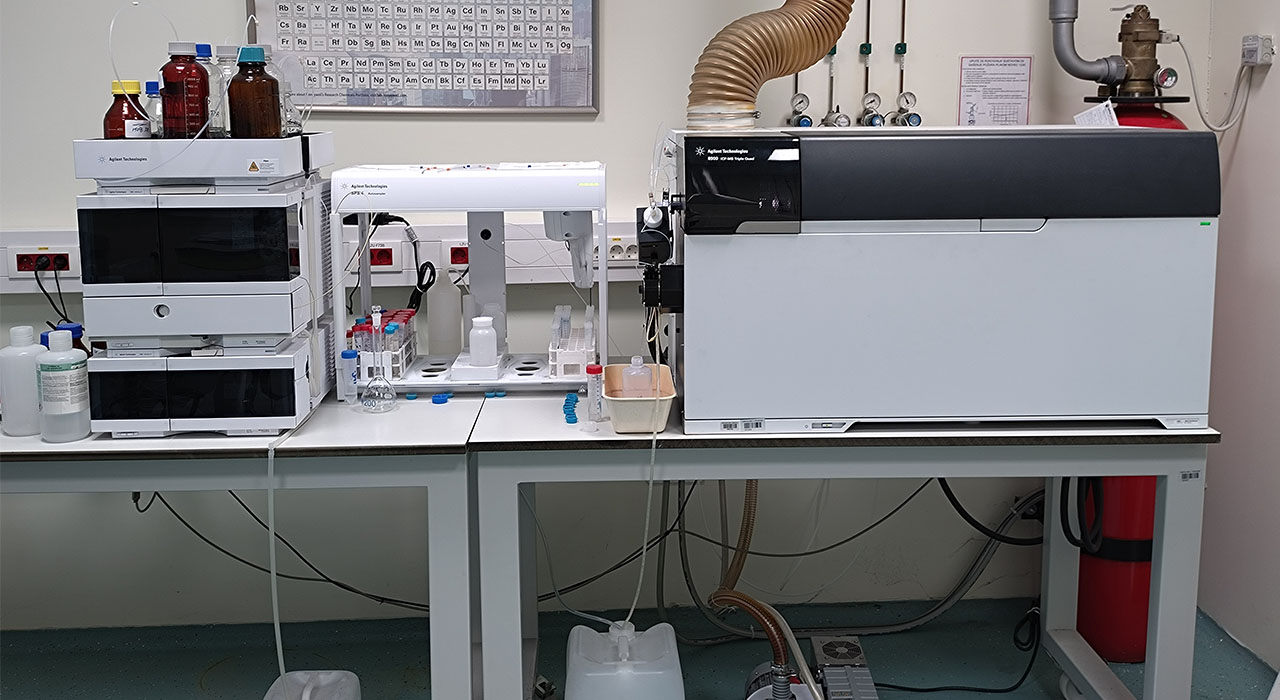


The activities of the Josip Juraj Strossmayer Water Institute focus, among other things, on cooperation with scientific and public institutions and participation in scientific research projects of strategic importance that promote knowledge-based development and sustainable development. Such co-operation promotes the involvement of experts and scientists in the implementation of scientific projects. One such example is the established cooperation with the Faculty of Medicine, University of Zagreb and other institutions in the field of healthcare in the preparation of a scientific article for the purpose of implementing a scientific project under the auspices of the Croatian Science Foundation under the leadership of Dr Filip Sedlić, Professor. The task of the Institute was to determine the concentration of elements that accumulate in human heart tissue due to environmental influences using the advanced ICP-MS method in the biomedical field. The research aimed to investigate the relationship between the concentrations of the elements Cu, Fe, Mn, Mo and Zn in the heart muscle and the mitochondrial response to misfolded proteins (UPRmt) and the age of patients who have received a heart transplant or a left ventricular assist device (ageHTx/LVAD). Since the elements considered are naturally occurring in the environment (water, food, soil, air) and are most commonly ingested by humans through water and food, their accumulation in human cardiac tissue and their effect on mitochondrial response is the subject of this work. The research results will be presented in a scientific article that will be published on 6 September 2024 in the International Journal of Molecular Sciences – MDPI under the title “Cardiotoxicity of Iron and Zinc and Their Association with the Mitochondrial Unfolded Protein Response in Humans” The results of the study show, among other things, a correlation between the cumulative concentrations of Fe and Zn in the myocardium and a lower age, when patients receive a heart transplant or LVAD, as well as increased cumulative concentrations of Fe and Zn in the myocardium, which may indicate accelerated heart failure.

Image 1. Agilent 8900 ICP-MS Triple Quad instrument in the Main Water Laboratory
Image 2. Implantable pump attached to the heart (LVAD) (taken from https://www.dicardiology.com)

Image 3. Scientific article “Cardiotoxicity of Iron and Zinc and Their Association with the Mitochondrial Unfolded Protein Response in Humans